MARHYS (MARine HYdrothermal Solutions)
A global compilation of hydrothermal vents (as of Dec 2020)
Abstract
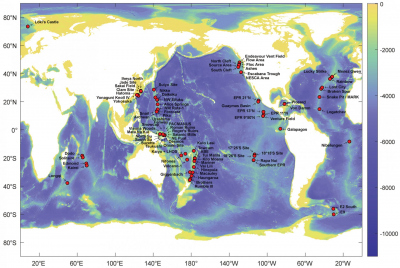
We introduce a database of hydrothermal vent fluid compositions extracted from peer-reviewed publications. The database includes general fluid parameters (e.g., temperature, salinity, and pH) as well as major-, minor-, and trace-element concentrations (including rare earth elements) of dissolved cations, anions, reduced carbon compounds, and gases. In addition, isotopic compositions of elements and molecules are included. Each parameter in the database is given in a uniform unit and enables direct intercomparison of data from the incorporated sources. The database provides detailed information about geographic location, the date of sampling, and a broad set of supplementary information that enables clear identification of each individual sample and the original data source. This type of metadata was used to merge compositional data for discrete vent fluid samples that originate from different publications. Hence, the database provides a more complete set of compositional parameters than the original sources do. To facilitate operability, the database is provided as ®Excel sheet, which enables users to visualize, sort, filter, and evaluate the database in a straightforward way. The sample information metadata enables extraction of available vent fluid data for specific regions, tectonic settings, host rock types, etc. The database will be a useful tool in determining (1) mechanisms that set fluid chemistry, as well as (2) regional and global geochemical fluxes across the seabed. To demonstrate the extent of the database, we examine the global distribution of magnesium, chloride, and sodium concentrations in vent fluid samples that are incorporated in MARHYS Database.




