- Home
- Discover
- Media Releases
- Media Releases 2023
- contourites
Deciphering the intensity of past ocean currents

Details of past climate conditions are revealed to researchers not only by sediment samples from the ocean floor, but also by the surface of the seafloor, which is exposed to currents that are constantly altering it. Deposits shaped by near-bottom currents are called contourites. These sediment deposits contain information about past ocean conditions as well as clues to climate. Contourites are often found on continental slopes or around deep-sea mountains. But they can be found in any environment where strong currents occur near the seafloor. The mechanisms that control them are not yet well understood. Experiments in flume tanks will help to change this through the depiction of deposition in future models.
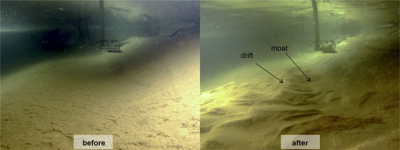
Detailed observations of changes in flume-tank experiments
Henriette Wilckens, first author of the newly published study, created a replica of the continental slope in a special flume tank at the University of Utrecht (Netherlands). Currents and sediment input in the flume tank were simulated using pumps and monitored with a current meter. The formation and development of the sediment deposits were measured with a laser scanner. All the data obtained were compared to measurements in natural ocean systems in order to validate the results of the experiments.
“The internal sediment architecture of contourites can be observed from seismic data, but in order to unlock information about the past ocean currents we need a better understanding of how they developed and the factors that influence the contourite systems,” explains Wilckens. While it is impossible to directly see how natural marine systems that developed over time periods of thousands to millions of years started to form on the seafloor, scientists can employ flume-tank experiments to directly observe detailed changes of the seafloor morphology and control their related current velocities.
Huge application potential of the models
“Our experiment can also be applied to the entire deep sea and even to lakes,” says Henriette Wilckens, meaning anywhere in the deep sea where there is a slope, terraces, deep-sea mountains or, for example, cold-water coral mounds.
It is also conceivable that the models could be applied, for example, to improve predictions of how currents transport microplastic particles or other pollutants in the ocean. “The potential for its application,” says Wilckens, “is immense. The system must first be understood before it is possible to derive information from it.”
Opening a new branch of research
“This research work is an important step toward a better understanding of the ways in which ocean currents control the deposition of particles in the seafloor, which has important implications for paleoceanographic reconstructions and benthic ecology. This introduces a new branch of research that will probably lead to even more exciting discoveries,” according to Elda Miramontes, co-author of the study and head of the “Sedimentology” working group at MARUM.
Original publication:
Henriette Wilckens, Joris T. Eggenhuisen, Pelle H. Adema, F. Javier Hernández-Molina, Ricardo Silva Jacinto & Elda Miramontes: Secondary flow in contour currents controls the formation of moat-drift contourite systems. Commun Earth Environ 4, 316 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-023-00978-0
Scientific contacts:
Dr. Henriette Wilckens
Sedimentology
MARUM – Center for Marine Environmental Sciences, University of Bremen
Email: [Bitte aktivieren Sie Javascript]
Prof. Dr. Elda Miramontes
Sedimentology
MARUM – Center for Marine Environmental Sciences, University of Bremen
Email: [Bitte aktivieren Sie Javascript]
Participating institutes:
- Faculty of Geosciences, University of Bremen, Germany
- MARUM – Center for Marine Environmental Sciences, University of Bremen, Germany
- Faculty of Geosciences, Utrecht University, The Netherlands
- Department of Earth Sciences, Royal Holloway University of London, UK
- Geosciences Department, CSIC & UGR, IACT, Spain
- MR 6538 GEO-OCEAN, Ifremer, Univ. Brest, CNRS, Université Bretagne Sud, France
MARUM produces fundamental scientific knowledge about the role of the ocean and the seafloor in the total Earth system. The dynamics of the oceans and the seabed significantly impact the entire Earth system through the interaction of geological, physical, biological and chemical processes. These influence both the climate and the global carbon cycle, resulting in the creation of unique biological systems. MARUM is committed to fundamental and unbiased research in the interests of society, the marine environment, and in accordance with the sustainability goals of the United Nations. It publishes its quality-assured scientific data to make it publicly available. MARUM informs the public about new discoveries in the marine environment and provides practical knowledge through its dialogue with society. MARUM cooperation with companies and industrial partners is carried out in accordance with its goal of protecting the marine environment.


