- Home
- RV Heincke HE 463 Expedition
RV Heincke HE 463 Expedition
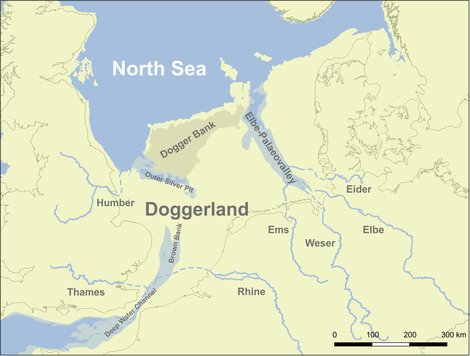
Postglacial drainage systems in the northern German Bight
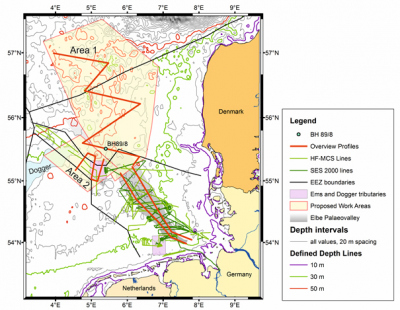
Location of the study areas in respect to the known position of the Elbe-Palaeovalley and the Dogger Bank. Magenta rectangles show the position of the Dogger drainage channel (north) and the Palaeo Ems (south). Existing MCS and SES lines in the German Bight are also shown. The red overview lines shall provide a first base for the exact location of a denser survey line network.
Organised by:


Groups involved:
- Department of Earth Science, University of Bergen, Norway (Prof. Haflidi Haflidason)
- Department of Geosciences and Natural Resource Management, University of Copenhagen, Denmark

Equipment:
- Highfrequency shallow water multichannel seismics
- Single channel seismic Boomer
- Echosounding systems
- Vibrocorer
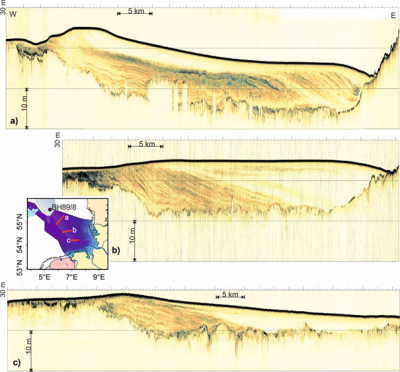
SES 2000 parametric subbottom profiler lines crossing the Elbe-Palaeovalley at three different latitudes as indicated in the inset. The images show a color coded display of the envelope of the recorded signal. The depth scale has been calculated assuming a sound velocity of 1500 m/s.
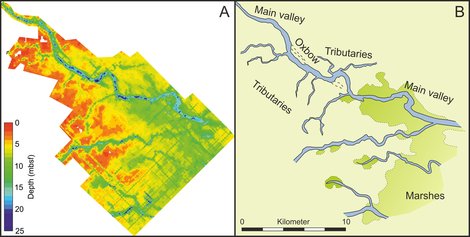
Fluvial system southeastern of the Dogger Bank: (A) Seismic visualization of the earliest Holocene palaeosurface and valley basis showing a complex fluvial system. (B) Interpretation of the seismic grid showing rivers, oxbows and bogland.
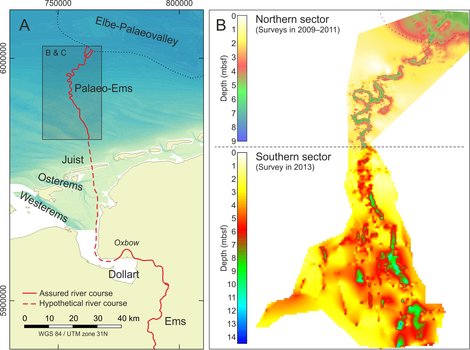
Paleo-Ems: (A) Assured river course of the hidden Palaeo-Ems and the modern Ems River in relation to the Elbe-Palaeovalley. The hypothetical course (dashed red line), connecting the present-day Ems estuary and the mapped palaeo fluvial system. (B) Map of the Holocene base outlining the river valley as mapped from seismic data.



